Irfan Mehmood
Sejong University, South Korea
Title: Resource-Conscious frameworks for Multimedia Content Summarization and Information Prioritization
Biography
Biography: Irfan Mehmood
Abstract
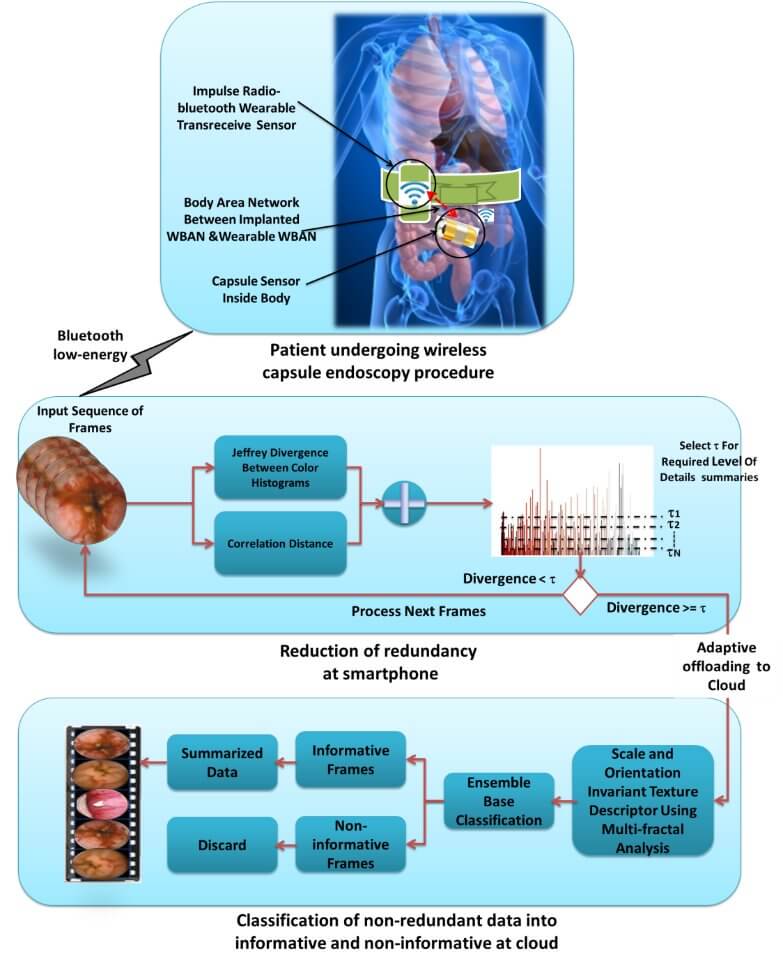
In recent years, there has been a tremendous increase in video capturing devices, which led to large personal and corporate digital video archives. This huge volume of video data became a source of inspiration for the development of vast numbers of applications such as visual surveillance, multimedia recommender systems, and context-aware advertising. The heterogeneity of video data, higher storage, processing cost, and communication requirements demand for a system that can efficiently manage and store huge amount of video data, while providing user-friendly access to stored data at the same time. To address this problem, multimedia summarization schemes have been proposed. Multimedia summarization refers to the extraction of keyframes, identifying most important and pertinent content. In various applications, video summarization can be conducted from the perspective of information prioritization, ranking chosen keyframes relative to their ability to describe the content of the video. A good video summary improves the effectiveness and efficiency of video archiving, cataloging, indexing, as well as increasing the usability of stored videos.
In this talk, video summarization in general and specifically in the context of prioritization (VSP) will be discussed. Varieties of algorithms, ranging from resource-conscious summarization framework to visual attention-based summarization methods are proposed. Four different VSP techniques are also proposed. The first summarization method is based on a light-weight visual attention model to efficiently extract diagnostically relevant keyframes from wireless capsule endoscopy videos. The second scheme proposes a resource-conscious summarization framework to manage remote sensing wireless capsule video data. The summarization is based on redundancy removal and classification of non-redundant frames into informative and non-informative frames. This framework utilizes cloud resources by adaptively offloading summarization tasks from mobile to cloud. The third and fourth proposed methods explore summarization in the context of prioritization in two different domains: 1) prioritization of brain magnetic resonance images; and 2) saliency-directed prioritization of visual data in wireless surveillance networks.