Day :
Keynote Forum
Ching Y Suen
Concordia University, Canada
Keynote: How well can computers recognize handwriting ?
Time : 10:05-10:35

Biography:
Ching Y. Suen is the Director of CENPARMI and the Concordia Honorary Chair on AI & Pattern Recognition. He received his Ph.D. degree from UBC (Vancouver) and his Master's degree from the University of Hong Kong. He has served as the Chairman of the Department of Computer Science and as the Associate Dean (Research) of the Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science of Concordia University. Prof. Suen has served at numerous national and international professional societies as President, Vice-President, Governor, and Director. He has given 45 invited/keynote papers at conferences and 200 invited talks at various industries and academic institutions around the world. He has been the Principal Investigator or Consultant of 30 industrial projects. His research projects have been funded by the ENCS Faculty and the Distinguished Chair Programs at Concordia University, FCAR (Quebec), NSERC (Canada), the National Networks of Centres of Excellence (Canada), the Canadian Foundation for Innovation, and the industrial sectors in various countries, including Canada, France, Japan, Italy, and the United States. Currently, he is the Editor-in-Chief of the journal of Pattern Recognition, an Adviser or Associate Editor of 5 journals, and Editor of a new book series on Language Processing and Pattern Recognition. Actually he has held previous positions as Editor-in-Chief, or Associate Editor or Adviser of 5 other journals. He is not only the founder of three conferences: ICDAR, IWFHR/ICFHR, and VI, but has also organized numerous international conferences including ICPR, ICDAR, ICFHR, ICCPOL, and as Honorary Chair of numerous international conferences.
Abstract:
Handwriting is one of the most important media of human communication. We write and read every day. Though handwriting can vary considerably in style and neatness, we recognize handwritten materials easily. Actually humans develop their writing skill in their childhood and gradually refine it throughout their lives. This paper examines ways humans write (from primary school to adult writing) and ways of teaching the computer to recognize (handwriting technology) what they produce from ancient (such as carved scripts, old books and documents) to modern times (such as immigration port-of-entry forms, cheques, payment slips, envelopes, and different kinds of notes and messages). Methods such a machine learning and deep classifier structures, extraction of space and margins, slant and line direction, width and narrowness, stroke connections and disconnections will be analyzed with large quantities of data. Both training procedures and learning principles will be presented to illustrate methodologies of enabling computers to produce robust recognition rates for practical applications in the office and in mobile phones. In addition, the art and science of graphology will be reviewed, and techniques of computerizing graphology will be illustrated with interesting examples.
Keynote Forum
Anton Nijholt
University of Twente , the Netherlands
Keynote: Playful Multimedia in Smart and Playable Cities
Time : 09:00-09:40

Biography:
Anton Nijholt received his PhD in computer science from the Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam. He held positions at various universities, both inside and outside the Netherlands. In 1989 he was appointed full professor at the University of Twente in the Netherlands. His main research interests are human-computer interaction with a focus on playful interfaces, entertainment computing, and humor generation. He edited various books, most recently on playful interfaces, entertainment computing and playable cities. Nijholt acted as program chair and general chair of many large international conferences on affective computing, entertainment computing, virtual agents, and multimodal interaction. He is chief editor of the section Human-Media Interaction of the journals Frontiers in Psychology, Frontiers in Digital Humanities, and Frontiers in ICT. He is co-editor of the Springer Book Series Gaming Media and Social Effects. Since 2015 he is also Global Research Fellow at the Imagineering Institute in Malaysia.
Abstract:
In research on smart cities the emphasis is on the use of sensors that collect information about a city’s inhabitants’ use of resources, their (real-time) behavior, and, using actuators, provide feedback to its citizens or a city’s management, and make changes to the environment that allow for more efficient use of a city’s resources . Management, efficiency and sustainability are keywords. Smartness in smart cities addresses ways to control energy consumption, increase safety, manage real-time traffic and public events, and manage other ways to make cities more efficient.
There is more to city life than efficiency. Sensors and actuators that make a city smart can be used to introduce smart playful and humorous situations, urban games, and other games that are meant to provide playful experiences or playful participation and contribution to urban design and development. Rather than have sensors and actuators to be introduced for making city life and management more efficient, they can as well be introduced to make city life more playful, increasing playfulness and introducing playful experiences during a citizen’s daily activities. We can talk about playful cities and when citizens are given the opportunity to introduce and configure sensor and actuator networks themselves we can also talk about playable cities.
Playable cities allow inhabitants to introduce their own playful applications. They need access to sensors, actuators and microprocessors. Introducing playfulness and humor in smart environments requires knowledge about humor theories. We discuss the theories and make a transition from the usual verbal humor theories to design principles that allow and stimulate the creation of humor in smart environments. We discuss accidental and intentional occurrences of humor and embed them in a framework of humor creation in smart and digitally enhanced physical environments.
- Virtual Reality| Animation and Simulations | Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition |Computer Graphics & Applications| Image Processing | Artificial Intelligence| 3D analysis, representation and printing |

Chair
Ching Y Suen
Concordia University, Canada

Co-Chair
Mort Naraghi-Pour
Louisiana State University, USA
Session Introduction
Mort Naraghi-Pour
Louisiana State University, USA
Title: Context-based unsupervised ensemble learning and feature ranking

Biography:
Mort Naraghi-Pour received his Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in 1987. Since August 1987, he has been with the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, where he is currently the Michel B. Voorhies Distinguished Professor of Electrical Engineering. From June 2000 to January 2002, he was a Senior Member of Technical Staff at Celox Networks, Inc., a network equipment manufacturer in St. Louis, MO. Dr. Naraghi-Pour received the best paper award from WINSYS 2007 for a paper co-authored with his student, Dr. X. Gao. Dr. Naraghi-Pour’s research and teaching interests include wireless communications, broadband networks, information theory, and coding. He has served as a Session Organizer, Session Chair, and member of the Technical Program Committee for numerous national and international conferences.
Abstract:
In ensemble systems, several experts, which may have access to possibly different data, make decisions which are then fused by a combiner (meta-learner) to obtain a final result. Such Ensemble-based systems are well-suited for processing Big-Data from sources such as social media, in-stream monitoring systems, networks, and markets, and provide more accurate results than single expert systems. However, most existing ensemble learning techniques have two limitations: i) they are supervised, and hence they require access to the true label, which is often unknown in practice, and ii) they are not able to evaluate the impact of the various data features/contexts on the final decision, and hence they do not learn which data is required. In this paper we propose a joint estimation-detection method for evaluating the accuracy of each expert as a function of the data features/context and for fusing the experts’ decisions. The proposed method is unsupervised: the true labels are not available and no prior information is assumed regarding the performance of each expert. Extensive simulation results show the improvement of the proposed method as compared to the state-of-the-art approaches. We also provide a systematic, unsupervised method for ranking the informativeness of each feature on the decision making process.
Ghyslain Gagnon
École de technologie supérieure, Université du Québec, Montreal, Canada
Title: The Circuit of Bachelard: a lumino kinetic interactive artwork Le Circuit de Bachelard: a lumino kinetic interactive artwork at École de technologie supérieure
Time : 12:05-12:30

Biography:
Ghyslain Gagnon received the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from Carleton University, Canada in 2008. He is now an Associate Professor at École de technologie supérieure, Montreal, Canada. He is an executive committee member of ReSMiQ and Director of research laboratory LACIME, a group of 10 Professors and nearly 100 highly-dedicated students and researchers in microelectronics, digital signal processing and wireless communications. Highly inclined towards research partnerships with industry, his research aims at digital signal processing and machine learning with various applications, from media art to building energy management.
Abstract:
This peculiar combination of illuminated electro-technical elements honors the intellectual journey of philosopher Gaston Bachelard (1884-1962), who interlaced forward-thinking ideas underlying the complex interaction of reason and imagination, an important contribution to inspire us a society deeply marked by scientific and artistic creativity. Permanently installed in the main tunnel at École de technologie supérieure, Montreal, Canada, this interactive artwork reminds future engineers of the importance of the rationale-intuitive bilaterality in any technological innovation.
The animation of lighting creates routes of running light blobs through the tunnel. Since the lighted tubes share the space with actual electrical and HVAC pipes, the lighting dynamics gives the impression of flow of useful elements (electricity, network data, air) in the building. A microphone is hidden in an electrical box at the center of the tunnel to allow interactive control. A sound recognition algorithm is used to identify blowing sounds: when users blow in an opening in this electrical box, the flow of light is accelerated, a symbol of the contribution of engineers in such technical systems.
The artwork was designed as an innovation platform, for students to add elements to the installation in the future, allowing increased interactivity. This platform was successfully tested in 2015 by a team who created a luminous tug of war game in the tunnel, with players using their mobile phones as a controlling device.
The installation was nominated at the Media Architecture Biennale awards ceremony, Sydney, 2016.
Mounîm A. El-Yacoubi
University of Paris-Saclay, Palaiseau, France
Title: Sequential modeling and recognition of human gestures and actions
Time : 13:45-14:10

Biography:
Mounîm A. El-Yacoubi (PhD,University of Rennes, France, 1996) was with the Service de Recherche Technique de la Poste (SRTP) at Nantes, France, from 1992 to 1996, where he developed software for Handwritten Address Recognition that is still running in Automatic French mail sorting machines. He was a visiting scientist for 18 months at the Centre for Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (CENPARMI) in Montréal, Canada, and then an associated professor (1998-2000) at the Catholic University of Parana (PUC-PR) in Curitiba, Brazil. From 2001 to 2008, he was a Senior Software Engineer at Parascript, Boulder (Colorado, USA), a world leader company in automatic processing of handwritten and printed documents (mail, checks, forms). Since June 2008, he is a Professor at Telecom SudParis, University of Paris Saclay. His main interests include Machine Learning, Human Gesture and Activity recognition, Human Robot Interaction, Video Surveillance and Biometrics, Information Retrieval, and Handwriting Analysis and Recognition.
Abstract:
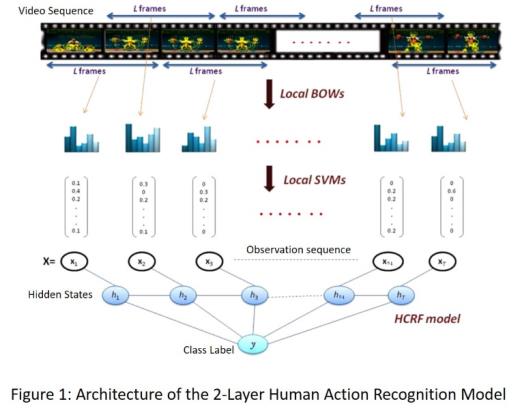
Human action recognition (HAR) is an active research field, driven by the dramatic price decrease of powerful digital cameras, storage and computing machines, and by the potential of HAR for designing smart engines making sense of today ubiquitous video streams. In video surveillance, for instance, HAR can help determining abnormal events in public facilities. For e-health, HAR may be harnessed as an assistive technology monitoring people with autonomy loss. Recognizing human actions, however, is challenging. Known variability factors such intra-class and inter-class variability, are much more adverse as they involve additional structural variability that is hard to cope with. Besides, actions are not communicative in general, which hinders relevant information acquisition and tracking. Others variability sources include viewing direction and distance w.r.t acquisition sensor, lighting conditions, etc. In this talk, we review the problem of human action and gesture recognition in general. After discussing the challenges above, we propose a new approach that focuses on video sequential input modeling. The modeling is based on a two-layer SVM – Hidden Conditional Random Field (SVM-HCRF) in which SVM acts as a discriminative front-end feature extractor. First, a sliding window technique segments the video sequence into short overlapping segments, described each by a local Bag-of-Words (BOW) of interest points. A first-layer SVM classifier converts each BOW into a vector of class conditional probabilities. The sequence of these vectors serves as the input observation sequence to HCRF for actual human action recognition. We show how this hierarchical modeling optimally combines two different sources of information characterizing motion actions: local motion semantics inferred by SVM, and long range motion feature dependencies modeled by HCRFs at a higher level. Finally, we show how these models can be extended to the problem of conjoint segmentation and recognition of a sequence of actions within a continuous video stream.
Nicole Vincent
Paris Descartes University, France
Title: Blur in text documents: Estimation and restoration
Time : 14:10-14:35

Biography:
Nicole Vincent has her expertise in Pattern Analysis Document. She is a Full Professor at Paris Descartes University, in SIP research group (Systèmes Intelligents de Perception) at LIPADE Lab. She completed her PhD in Computer Science in 1988 and became Full Professor in 1996. She worked in numerous projects in pattern recognition, signal and image processing and understanding and video analysis with particular interest for document image analysis domain. She has supervised more than 35 students and collaborated with many labs, institutions and companies.
Abstract:
Document transfers are more and more often achieved in an electronic way and images come from mobile camera. Then, image quality varies a lot and is no more mastered. An important first step in next processing is to evaluate the quality, blur is adding noise. In this context, blur model is difficult to apply as it has different origins, defocusing or movement blur. Models are often suited for one type of blur and when blur is uniform on the whole page. Then some learning can enable to solve a reverse problem. Some other approach can be developed that adapts itself locally to the image content. On a document, all parts are not equivalent and textual parts are more important from blur point of view than figure parts or background parts; for example, blur is based on the ambiguity coming from the pixel color associated with text part and background. Thus, fuzzy model is suited to interpret the color level distribution in the neighborhood of text contours. Fuzzy clustering leads to two classes and a fuzzy score can be defined at a pixel level from the membership values, the results can be propagated at higher levels. The interest of the approach is two-fold, quality can be estimated and the contrast in the document can be improved. Evaluation can be performed from different points of view, from an aesthetical point of view, that is human perception or in a quantitative way. The approach can be direct or indirect. In document analysis, optical character recognition is, most often, the main objective on which relies the future processing and the understanding phase. Then, improving OCR recognition rate is one way to measure the de-blurring process. Comparison with other methods can be performed on public databases, in our case on DIQA database.


Nuria Medina-Medina
University of Granada, CITIC-UGR, Spain
Title: Designing video games
Time : 14:35-15:00

Biography:
Nuria Medina received her Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Granada (UGR) in 2004, proposing an adaptive and evolutionary model for hypermedia systems. Nowadays, she belongs to the direction team of the Research Centre for Information and Communications Technologies (CITIC-UGR) and is professor at the Department of Computer Languages and Systems at this Spanish University where she directs a project that implements educational games in Andalusian school classrooms (P11-TIC7486).
Abstract:
The video game industry continues with its high rate of growth and, correspondingly, video games are a product present in most of the first-world households. Thousands of people around the planet work in the development of games and billions of players enjoy these multimedia creations; however, from an engineering perspective, critical issues in the design of these video games are not are being sufficiently considered. Therefore, an academic effort to identify and analyze which are the keys of a good design and the possible design solutions in each particular context should be done in relation to the productive and unstoppable world of video games. With this aim, taxonomies, guidelines and design patterns are different approaches in which we have been working. On the other hand, serious games must be specially attended since the serious propose involved in the game implies the need to design and integrate no-ludic contents and the collaboration with no-technical professionals during all the process. In the first case, it is essential to introduce the serious elements in the game so that they remain hidden within the ludic contents. In the second case, an adequate language is crucial to facilitate the communication between the technical team and the subject-domain experts (educators, doctors, etc.). Particularly, our group has been researching to achieve the indispensable balance between the ludic component and the instructive component in educational video games. As a result, our design methodology establishes a ‘divide and conquer' approach where the game challenges and the educational goals are designed and interrelated making use of graphics notations, which allow modeling of the artefacts of the educational video game in a comprehensible form for all the stakeholders. As a study case, an educational adventure to promote reading comprehension has been developed and is being evaluated.
Stylianos (Stelios) Asteriadis
University of Maastricht, the Netherlands
Title: Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence to the service of societal needs
Time : 15:00-15:25

Biography:
Stylianos Asteriadis, PhD, MSc, is Assistant Professor at the University of Maastricht, the Netherlands. Stylianos Asteriadis received his PhD from the School of Electrical and Computer Eng. of National Technical University of Athens. His research interests lie in the areas of affective computing, visual computing, machine learning, and human activity recognition, while he has published more than 40 journal and international conference papers in the aforementioned fields. Currently, he is the Principal Investigator for the University of Maastricht in two H2020 collaborative projects (H2020-PHC-2015 Health project ‘ICT4Life- Advanced ICT systems and services for integrated care’ and H2020 ICT-20-2015 ‘MaTHiSiS- Technologies for better human learning and teaching’), while he is a reviewer and program committee member for several journals and conferences in his field
Abstract:
Recent advances in the areas of computer vision, artificial intelligence and data analysis are giving rise to a new era in human-machine interaction. A computer (or a machine, in general) should not be seen as a passive box that just processes information but, instead, today it can – and, actually, should - be seen as a device that can act as a companion, an active tutor or a health coach that can interpret our personalized needs, emotions and activities. Coupling human-machine interaction with ambient assisted living and visual computing is now escaping the tight limits of research laboratories and university departments and real products see their way into the market. We discuss about our current research in the use of computer vision and latest advances in machine intelligence to the benefit of societal needs and, in particular, in the areas of education and health. We will present the pipeline and methods used in our research, as well as the bottlenecks met, both from a technical point of view and a functional one. Subsequently, we will give an overview of computer vision techniques and ambient assisted living technologies utilized for human emotion understanding and activity recognition. Results, within the frame of our current work, with the use of ANNs for learning, in an unsupervised manner, personalized patterns in emotion and/or activity understanding, user profiling and system adaptation will be shown and discussed during the talk.
Arata Kawamura
Osaka University, Japan
Title: Image to sound mapping and its processing techniques
Time : 15:25-15:50

Biography:
Arata Kawamura completed BE and ME degrees in Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Tottori University, Japan, in 1995 and 2001, respectively, and DE degree at Osaka University, Japan, in 2005. He was an Assistant Professor at Osaka University from 2003 to 2012. He is currently an Associate Professor at Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Japan. His main researches are in the area of Speech Signal Processing. Recently, his research interests include image processing, especially image to sound mapping. He developed a transformation method from an image to an understandable human speech signal in 2016. He is studying to process a sound as an image, or an image as a sound.
Abstract:
Sound spectrogram is useful to visually analyze time-varying characteristics of a sound. Since the sound spectrogram can be treated as an image, we can process the sound spectrogram by using image processing techniques. Such interesting techniques have been applied in music transcription, musical instruments sound separation, noise reduction and so on. Conversely, we can produce a sound signal from an image which is treated as a sound spectrogram. This technique is called as image to sound mapping. In the image to sound mapping, the most important parameters are spectral phase, playback time and frequency bandwidth. The spectral phase decides sound type or tone color. The playback time is the time for providing the single image, and frequency bandwidth decides each pitch of sinusoid to make the sound. Since the main purpose of the mapping sound is to bear the image as a sound, we should carefully make the mapping sound under a common condition with respect to these parameters. Addition to it, we should have some knowledge of a filtering effect for the mapping sound, because the sound is received at sensors after passing through a certain transfer function from a loudspeaker to the sensors. I focus on filtering or modifying a mapping sound from an image, and investigate its image-reconstruction capability. Firstly, we review image to sound mapping techniques. Secondly, for a mapping sound, we apply three basic operations of the signal processing, i.e., multiplication, delay, and addition. Thirdly, we discuss the basic filtering effects obtained from low-pass filters, high-pass filters, and band-pass filters. These processing results are intuitively acceptable. Then, we also investigate FIR and IIR echo effects. After that, some modulation effects such as amplitude modulation are discussed. Finally, on a sound to image mapping method, useful drawing techniques are presented.
Jehan Janbi
Taif University, KSA
Title: PANOSE-A: Encoding Arabic Fonts based on design characteristics
Time : 16:10-16:35

Biography:
Jehan Janbi is an assistance professor in Computer Science and Information Technology College at Taif University. She got her bachelor of Computer Science from King Abdul-Aziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. She started her Academic career journey as TA lab supervisor and research assistance in Computer Science department in Qassim University. She upgraded her academic level and got her Master and PhD from Concordia University, Montreal, Canada. Her research area is in text and font recognition, mainly for Arabic script. She worked on encoding Arabic digital font’s design characteristics into a number composed of several digits where each digit represents specific design characteristics. This will enhance manipulating and searching fonts based on their appearance.
Abstract:
In digital world, there are thousands of digital fonts makes selecting an appropriate font is not an intuitive issue. Designers can search for a font like any other file using general information such as name and file format. But for document design purposes, the design features or visual characteristics of fonts are more meaningful for designers than font file information. Therefore, representing fonts’ design features by searchable and comparable data would facilitate searching and selecting a desirable font. One solution is to represent a font’s design features by a code composed of several digits. This solution has been implemented as a computerized system called PANOSE-1 for Latin script fonts. It is used within several font management tools as an option for ordering and searching fonts based on their design features. It is also used in font replacement processes when an application or an operating system detects a missing font in an immigrant document or website. This research defined a new model, PANOSE-A, to extend PANOSE-1 coverage to support Arabic characters. The model defines eight digits in addition to the first digit of PANOSE-1which indicates the font script and family type. Each digit takes value between 0-15 where each value indicates a specific variation of its represented feature. Two digits of the models describe the common variations of the weight and contrast features, which are two essential features in any font design. Another four digits describe the shape of some strokes that usually vary in their design between fonts, such as the end shape of terminal strokes, the shape of the bowl stroke, the shape of curved stroke and the shape of rounded strokes with enclosed counter. The last two digits describe the characteristics of two important vertical references of the Arabic font design which are tooth and loop heights.
Tsang-Ling Sheu
National Sun-Yat-Sen University, Taiwan
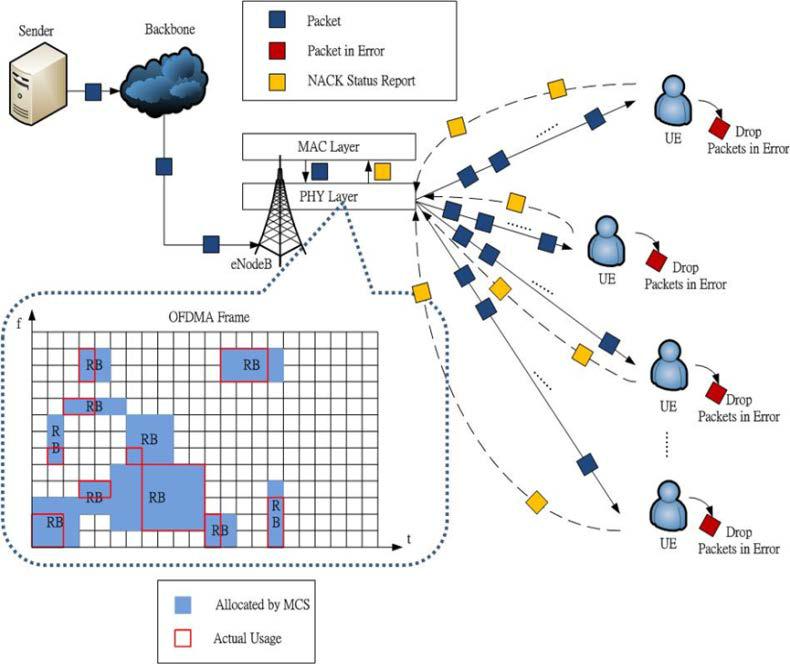
Title: Dynamic RB allocations using ARQ status reports for multimedia traffic in LTE networks
Time : 16:35-17:00

Biography:
Tsang-Ling Sheu received the Ph.D. degree in computer engineering from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Penn State University, University Park, Pennsylvania, USA, in 1989. From Sept. 1989 to July 1995, he worked with IBM Corporation at Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, USA. In Aug. 1995, he became an associate professor, and was promoted to full professor in Jan. 2006 at the Dept. of Electrical Engineering, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. His research interests include wireless networks, mobile communications, and multimedia networking. He was the recipient of the 1990 IBM outstanding paper award. Dr. Sheu is a senior member of the IEEE, and the IEEE Communications Society.
Abstract:
This paper presents a dynamic resource blocks (RBs) allocation scheme for multimedia traffic in LTE networks by utilizing automatic repeated request (ARQ) status report, in which an user equipment (UE) reports erroneous packets to an evolved-node base station (eNodeB). From the status report, eNodeB will compute the amount of successfully received packets per unit time for each UE. Therefore, eNodeB can properly allocate RBs which is exactly the requirement of each UE. Moreover, we consider three different multimedia traffic types (audio, video, and data) with different priorities. Our proposed scheme can alter the modulation determined by automatic modulation and coding (AMC) scheme such that the utilization of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing access (OFDMA) frame can be substantially increased. To prevent the starvation of data traffic which has the lowest priority, we set an upper bound of employed RBs for audio and video traffic. At last, we perform NS-3 simulation to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed scheme. The simulation results show that our proposed scheme can perform much better than the traditional AMC scheme in terms of RBs utilization, blocking rate of UEs, and the number of successfully connected UEs. Particularly, when in a high noise environment and a large number of UE under an eNodeB, the proposed scheme can achieve relatively smaller blocking rates for QoS-guaranteed multimedia traffic, such as video and audio.
Yea-Shuan Huang
Huang-Hua University, Taiwan
Title: Feature-point geometrical face recognition with local invariant features
Time : 17:00-17:25

Biography:
Abstract:
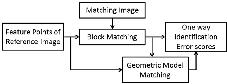
Maria Jose Arrojo
University of A Coruña, Spain
Title: Procedures for searching information on the Internet. Role of designs based on Artificial Intelligence

Biography:
Maria Jose Arrojo is reader at the Department of Humanities of the University of A Coruña. She has the recognition as Titular Professor in the field of Communication Sciences. She is member of the research group that works on the philosophy and methodology of the Sciences of the Artificial. She has published papers analyzing communication sciences from the perspective of the sciences of the artificial, in general, and the design sciences, in particular. Arrojo has been working off research projects on bounded rationality and the sciences of design supported by the Spanish Ministry related to scientific research and technological innovation. Since 2003 she is the co-director of the Post-degree studies in Audiovisual Production and Management at the University of A Coruña. She was an advisor to the Institute for Foreign Trade of the Government of Spain, in strategic issues of the internationalization of the audiovisual sector (2005-2011).
Abstract:
The procedures for finding information on the Internet are mediated by three main aspects. First, the mode of representation of knowledge, because the search is done by a conceptual content that guides the search designs. Second, the specific procedures of heuristics, that is, the patterns or rules that agents or machines must follow so that they have adequate programming to achieve the results they are looking for. Third, there is the task of the agents, who are the ones who select the aims, choose the procedures and evaluate the results.
All of this is done in the procedures for searching information on the Internet. This is possible by designs based on Artificial Intelligence. The study of these designs requires research from the Artificial Sciences. In this sense, this paper starts from the base of the Communication Sciences conceived as Applied Sciences of Design, therefore of the Sciences of the Artificial. Thus, the epistemological point of departure is the representation of knowledge that set aims, which in this case are forms of information on the Internet (YouTube, Snapchat, etc.). Then the methodological component comes, specific ways of finding the information based on the objectives sought with the designs. Thirdly, we have the ontological factor, where agents intervene to achieve the results, based on the representation of knowledge and search methods
It is assumed here that, to design the machine learning procedure, the starting point of the designs is in Artificial Intelligence. To that end, it is necessary to be clear what the objectives of the search are, to reach the aims drawn with the design. Only then do the machines finish doing what they have been programmed for. The agents intervene at the beginning, for the design aims, and at the end, to evaluate the results obtained.
Chengjiang Long
Kitware Inc, USA
Title: Collaborative Active Learning from Crowds for Visual Recognition

Biography:
Chengjiang Long received his Ph.D. degree from Stevens Institute of Technology in 2015. Currently, he is a computer vision researcher in the computer vision team at Kitware, a leader in the creation and support of state-of-the-art technology, providing robust solutions to academic and government institutions, such as DARPA, IARPA, and the Army, as well as private corporations worldwide. Prior to joining Kitware, he ever worked at NEC Labs America and GE Global Research in 2013 and 2015, respectively. To date, he has published more than 20 papers in reputed international journals and conferences, and has been searving as a reviewer for top international journals (e.g., TIP, MM, MVAP and TVCJ) and conferences (e.g., ICCV, ECCV, ACCV, BMVC and ICME).
Abstract:
Active learning is an effective way to relieve the tedious work of manual annotation in many applications of visual recognition. The vast majority of previous works, if not all of them, focused on active learning with a single human oracle. The problem of active learning with multiple oracles in a collaborative setting has not been well explored. Moreover, most of the previous works assume that the labels provided by the human oracles are noise free, which may often be violated in reality.
To solve the above-mentioned issues, we proposed two models (i.e., a distributed multi-labeler active learning model and a centralized multi-labeler active learning model) for collaborative active visual recognition from the crowds, where we explore how we can effectively model the labelers’ expertise in a crowdsourcing labeling system to build better visual recognition models. Both two models are not only robust to label noises, but also a principled label quality measure to online detect irresponsible labelers. We also extended the centralized multi-labeler active learning model from binary cases to multi-class cases and also incorporate the idea of reinforcement learning to actively select both the informative samples and the high-quality annotators, which better explores the trade-off between exploitation and exploration.
Our collaborative active learning models have been validated in the real-world visual recognition benchmark datasets. The experimental results strongly show the validity and efficiency of the two proposed models.

Biography:
Abstract:
Syed Afaq Ali Shah
The University of Western Australia, Australia
Title: Deep learning for Image set based Face and Object Classification
Biography:
Syed Afaq Ali Shah has done PhD in 3D computer vision (feature extraction, 3D object recognition, reconstruction) and machine learning in the School of Computer Science and Software Engineering (CSSE), University of Western Australia, Perth. He was holder of the most competitive Australian scholarships, which include Scholarship for International Research Fee (SIRF) and Research Training Scheme (RTS). He has published several research papers in high impact factor journals and reputable conferences. Afaq has developed machine learning systems and various feature extraction algorithms for 3D object recognition. He is the reviewer for IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, Journal of Real Time Image Processing and IET Image Processing journal.
Abstract:
I shall present a novel technique for image set based face/object recognition, where each gallery and query example contains a face/object image set captured from different viewpoints, background, facial expressions, resolution and illumination levels. While several image set classification approaches have been proposed in recent years, most of them represent each image set as a single linear subspace, mixture of linear subspaces or Lie group of Riemannian manifold. These techniques make prior assumptions in regards to the specific category of the geometric surface on which images of the set are believed to lie. This could result in a loss of discriminative information for classification. The proposed technique alleviates these limitations by proposing an Iterative Deep Learning Model (IDLM) that automatically and hierarchically learns discriminative representations from raw face and object images. In the proposed approach, low level translationally invariant features are learnt by the Pooled Convolutional Layer (PCL). The latter is followed by Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) applied iteratively in a hierarchical fashion to learn a discriminative non-linear feature representation of the input image sets. The proposed technique was extensively evaluated for the task of image set based face and object recognition on YouTube Celebrities, Honda/UCSD, CMU Mobo and ETH-80 (object) dataset, respectively. Experimental results and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods show that our technique achieves the best performance on all these datasets.

Biography:
David Zhang graduated in Computer Science from Peking University. He received his MSc in 1982 and his PhD in 1985 in Computer Science from the Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT), respectively. From 1986 to 1988 he was a Postdoctoral Fellow at Tsinghua University and then an Associate Professor at the Academia Sinica, Beijing. In 1994 he received his second PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. He is a Chair Professor since 2005 at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University where he is the Founding Director of the Biometrics Research Centre (UGC/CRC) supported by the Hong Kong SAR Government in 1998. He also serves as Visiting Chair Professor in Tsinghua University, and Adjunct Professor in Peking University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, HIT, and the University of Waterloo. He is Founder and Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Image and Graphics (IJIG); Founder and Series Editor, Springer International Series on Biometrics (KISB); Organizer, the 1st International Conference on Biometrics Authentication (ICBA); Associate Editor of more than ten international journals including IEEE Transactions and so on. So far, he has published over 10 monographs, 400 journal papers and 35 patents from USA/Japan/HK/China. According to Google Scholar, his papers have got over 34,000 citations and H-index is 85. He was listed as a Highly Cited Researcher in Engineering by Thomson Reuters in 2014 and in 2015, respectively. Professor Zhang is a Croucher Senior Research Fellow, Distinguished Speaker of the IEEE Computer Society, and a Fellow of both IEEE and IAPR.
Abstract:
In recent times, an increasing, worldwide effort has been devoted to the development of automatic personal identification systems that can be effective in a wide variety of security contexts. As one of the most powerful and reliable means of personal authentication, biometrics has been an area of particular interest. It has led to the extensive study of biometric technologies and the development of numerous algorithms, applications, and systems, which could be defined as Advanced Biometrics. This presentation will systematically explain this new research trend. As case studies, a new biometrics technology (palmprint recognition) and two new biometrics applications (medical biometrics and aesthetical biometrics) are introduced. Some useful achievements could be given to illustrate their effectiveness.

Biography:
We are also accepting proposals for Symposia and Workshops on all tracks. All proposals must be submitted to multimedia@conferenceseries.net
Abstract:

Biography:
David Xu is tenure associate professor at Regent University, specializing in computer 3D animation and movie special effects. He got MFA Computer Graphics in 3D Animation from Pratt Institute in NY. He has served as a senior 3D animator in Sega, Japan; a senior CG special effector in Pacific Digital Image Inc., Hollywood; and as a professor of animation in several colleges and universities where he developed the 3D animation program and curriculum. He has been a committee member of the computer graphics organization Siggraph Electronic Theater, where he was recognized with an award for his work.
Abstract:
Blend shapes, also known as morph target animation, are a powerful way of deforming geometry such as human face to create various facial expressions, from happy to sad. In this presentation, after overviewing Autodesk Maya blend shapes, their features and work flow, Professor Xu will demonstrate and discuss how to create a more efficient workflow by combining blend shapes with Maya’s Set Driven Key features, and how to create a more complex facial animation with advanced blend shape techniques and features. Concepts and techniques such as blend shape deformer, Blend Shape node, Tweak node, Set Driven Key, morph target animation, vertex position, and more will be introduced and demonstrated. Finally, Professor Xu will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using morph target animation over skeletal animation in 3D facial animation.
- Workshop
Session Introduction
Mounîm A El-Yacoubi
University Paris Saclay, France
Title: Can handwriting analysis be helpful for Alzheimer detection?

Biography:
Mounîm A. El-Yacoubi (PhD,University of Rennes, France, 1996) was with the Service de Recherche Technique de la Poste (SRTP) at Nantes, France, from 1992 to 1996, where he developed software for Handwritten Address Recognition that is still running in Automatic French mail sorting machines. He was a visiting scientist for 18 months at the Centre for Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (CENPARMI) in Montréal, Canada, and then an associated professor (1998-2000) at the Catholic University of Parana (PUC-PR) in Curitiba, Brazil. From 2001 to 2008, he was a Senior Software Engineer at Parascript, Boulder (Colorado, USA), a world leader company in automatic processing of handwritten and printed documents (mail, checks, forms). Since June 2008, he is a Professor at Telecom SudParis, University of Paris Saclay. His main interests include Machine Learning, Human Gesture and Activity recognition, Human Robot Interaction, Video Surveillance and Biometrics, Information Retrieval, and Handwriting Analysis and Recognition.
Abstract:
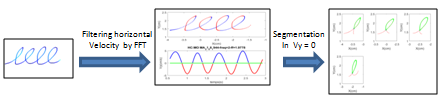
Figure 1: Segmentation of a 4l series into individual loops.
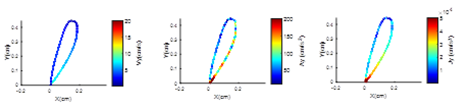
Figure 2: Evolution over l loop of vertical speed, acceleration, and jerk, from blue (low) to red (high).
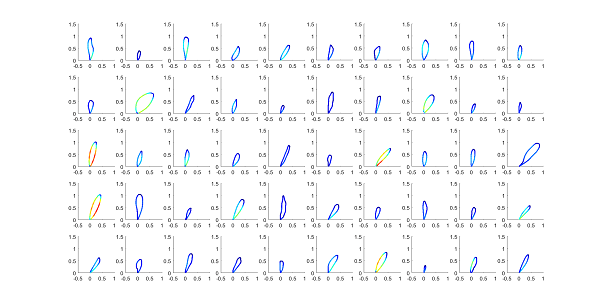
Figure 3: Medoids of the loops based on their speed dynamics.
- Multimedia applications and services | Multimedia communications and networking | Virtual Reality | Computer Games Design & Development | Visualization & Human Computer Interaction | Audio, Video, Speech & Signal Processing| Multimedia & AI in Healthcare
Session Introduction
Leonel Antonio Toledo DÃaz
Barcelona Supercomputer Center, Spain
Title: Interactive complex virtual environments using XML configuration files
Time : 11:40-12:05

Biography:
Leonel Toledo recieved his Ph.D from Instituto Tecnológico de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey Campus Estado de México in 2014, where he was a full-time professor from 2012 to 2014. He was an assistant professor and researcher and has devoted most of his research work to crowd simulation and visualization optimization. He has worked at the Barcelona Supercomputing Center using general purpose graphics processors for high performance graphics. His thesis work was in Level of detail used to create varied animated crowds. Currently he is a researcher at Barcelona Supercomputer Center.
Abstract:

Aykut Koc
ASELSAN Research Center, Turkey
Title: Pattern recognition for architecture: Identifying interior styles and scene components from images
Time : 12:05-12:30

Biography:
Aykut Koc completed his BS in Electrical Engineering at Bilkent University in 2005; PhD in Electrical Engineering, MS in Electrical Engineering and MS in Management Science at Stanford University. Following his PhD, he worked briefly in the Silicon Valley and then started to work for ASELSAN. He was in the founding team of ASELSAN Research Center and worked on its initial founding process from ground up. He is currently managing one of the research departments of ASELSAN Research Center, which can be considered a pioneer for corporate research labs in Turkey. He also teaches Fourier Optics course part-time at Middle East Technical University (METU), Electrical Engineering department. Throughout his career, he worked on digital algorithms for optics and image processing, visual target tracking algorithms as well as natural language processing.
Abstract:
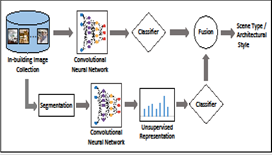
The vast amount of user uploaded visual content available online makes automated visual classification a critical research problem. While existing studies for visual classification mainly focus on recognition of generic objects such as vehicles, plants, food and animals, recently, studies have also been presented for exploring a more challenging research problem, fine grained object classification, aiming to distinguish fine subcategories within coarse object categories, such as types of vehicles, flowers and kinds of food. Here, another fine grained categorization problem important for multimedia applications, categorizing in-building scenes and their architectural styles, is attempted which will be beneficial for applications related to real estate and interior decoration. In-building scenes are divided into five coarse categories; kitchen, bathroom, living room, bedroom and dining room. As fine categories, each in-building scene has been assigned an architectural style such as Asian, Contemporary, Victorian, Rustic and Scandinavian. On a database consisting of a large number of in-building images, descriptive patterns corresponding to types of scenes and specific architectural styles are learned globally by utilizing deep convolutional neural network based models that have proven success in visual categorization. Moreover, local scene elements and objects which provide further clues for identifying architectural styles are discovered: Scene objects with unique architectural style characteristics carry more discriminative power, whereas co-existing objects visible among various types of scenes are less discriminative. As potential useful applications, several scenarios for classification and retrieval of in-building images are investigated. Experiments show that using only the learned deep representations are effective in identifying scene types while they perform poorly for architectural styles. Nonetheless, revealing key local scene objects ameliorates their performance for both classification and retrieval tasks for architectural styles.
J J Joshua Davis
The Embassy of Peace, New Zealand
Title: Learning about higher cognitive functions through the art of encephalography and brain dynamics movies
Time : 13:20-13:45

Biography:
J J Joshua Davis is experienced as a Decision Analyst and Strategic Planner for banks, oil companies, consulting firms and family business. He lectured for several years in the fields of Systems Thinking, Computer Simulation, Chaos Theory, Fractal Geometry, Decision Making and Systems Dynamics. From 1994 onwards, after a set of meaningful spiritual experiences, he spent many years travelling as an Ambassador of Peace around the world. Since 1998, he has worked in research concerning decision making and consciousness and published a thesis, “The Brain of Melchizedek, A Cognitive Neuroscience Approach to Spirituality”. More recently, he has been researching in close collaboration with Grant Gillett, Robert Kozma, Walter Freeman and Paul Werbos in the areas of Cognitive Neuroscience, Philosophy, Quantum Physics and Biophysics of Peace.
Abstract:
This presentation describes the development and use of the art of encephalography in a new and more advanced way, whereby this qualitative tool where large quantities of brain data images are processed and converted into brain dynamics movie and then displayed for the purpose of visual discrimination associated with the different brain cognitive states, as well as the different stages of cognitive processes related to the cycle of creation of knowledge and meaning. The methodology we present is inspired by the art of encephalography, where this art is enhanced from the mere plotting of brain signals in the time domain to spatio-temporal frames that when presented in a sequence of plots, produces a brain dynamics movie which allows to visualize different patterns of behavior in different conditions produced by different stimuli based on experimental data. By careful observation of each of these movies, we learn to identify different structures and visual patterns where large-scale synchronizations and de-synchronizations are observed across different frequency bands. These movies also allow us to explore the temporal evolution of these spatial brain patterns where we can identify the different stages in the manifestation of the hypothesized cycle of creation of knowledge and meaning. We conjecture that movie viewing, will allow a better understanding of learning and adaptation. In summary, we can say that viewing brain dynamics movies will allow a significant impression of: Brain events for different measurement; brain events across bands and; the different stages of the cycle of creation of knowledge and meaning. The research team at The Embassy of Peace in Whitianga, New Zealand accomplished this work in close collaboration with Walter J. Freeman and Robert Kozma.

Takayoshi Iitsuka
The Whole Brain Architecture Initiative, Japan
Title: Training long history on real reward and diverse hyper parameters in threads combined with DeepMind’s A3C+
Time : 13:45-14:10

Biography:
Takayoshi Iitsuka completed his Master's degree in Science and Technology at University of Tsukuba in Japan. From 1983 to 2003, he was a Researcher and Manager of optimizing and parallelizing compiler for supercomputers in Central Research Laboratory and Systems Development Laboratory of Hitachi. From 2003 to 2015, he was in strategy and planning department of several IT divisions. He retired Hitachi in October 2015 and started study and research of Artificial Intelligence in May 2016. In October, he achieved top position of Montezuma’s revenge in OpenAI gym. His current research interests include Deep Learning, Deep Reinforcement Learning and Artificial General Intelligence based on whole brain architecture.
Abstract:
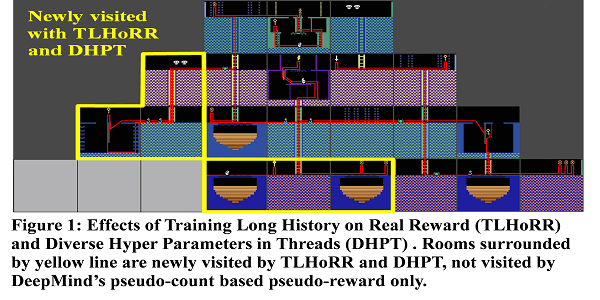
Games with little chance of scoring such as Montezuma’s revenge are difficult for Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) because there is little chance to train Neural Network (NN), i.e. no reward, no learning. DeepMind indicated that pseudo-count based pseudo-reward is effective for learning of games with little chance of scoring. They achieved over 3000 points in Montezuma’s revenge by combination with Double-DQN. On contrary, its average score was only 273.70 point in combination with A3C (it is called A3C+). A3C is very fast training method and getting high score with A3C+ is important. I propose new training methods: Training Long History on Real Reward (TLHoRR) and Diverse Hyper Parameters in Threads (DHPT) for combination with A3C+. TLHoRR trains NN with long history just before getting score only when game environment returns real reward i.e. training length by real reward is over 10 times longer than that of pseudo-reward. This is inspired by reinforcement of learning with dopamine in human brain. In this case, real score is very valuable reward in brain and TLHoRR strongly trains NN like dopamine does. DHPT changes hyper parameters of learning in each thread and make diversity in threads actions. DHPT was very effective for stability of training by A3C+. Without DHPT, average score is not recovered from zero when it is dropped to zero. With TLHoRR and DHPT in combination with A3C+, average score of Montezuma’s revenge almost reached 2000 points. This combination made exploration of game state better than that of DeepMinds’s paper. In Montezuma’s revenge, five rooms are newly visited by TLHoRR and DHPT; they were not visited by DeepMinds’s pseudo-count based pseudo-reward only. Furthermore, with TLHoRR and DHPT in combination with A3C+, I got and kept top position in Montezuma’s revenge in OpenAI gym environment from October 2016 to March 2017.
Mrouj M Almuhajri
Saudi Electronic University, KSA
Title: The impact of utilizing Twitter in the e-learning process: The comprehension of taught materials and the communication between college students
Time : 14:10-14:35

Biography:
Mrouj M Almuhajri is a Lecturer at Saudi Electronic University, KSA. She completed her Bachelor degree in Computer Science at Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia and, Master degree in Computer Science at Concordia University, Montreal, Canada.
Abstract:
Social media play a significant role among younger generations and students. They use it to communicate with the public, spread news, and share their thoughts using different content forms like text, audio, image, and video. Multimedia makes the transfer of information much easier. This paper details the results of a semester-long experiment that detect the effects of integrating Twitter with e-learning tools on the education process. More specifically, the experiment studies the ability to enhance the students’ understanding of the taught material and improve communication between the students and the instructor. The study was done in participation with sophomore SEU students taking CS141 (computer programming) and IT241 (operating systems) courses for computing and informatics majors. The study was conducted using the Twitter account @seugeeks. A total of 114 subscribers followed the account during the semester of the study. Twitter account was used for many activities, such as announcements, video tutorials, questions, and discussions. To assess the impact of using twitter in the teaching process, an online survey was published at the conclusion of the semester. A total of 39 students participated in the survey. The results reflected that all participants have twitter account, and the majority of them (65%) were using it for more than three years. Statistical analysis of Likert scale data revealed positive results of utilizing Twitter in the learning process. Both students and instructor were able to communicate with each other in an easier way creating a collaborative environment. In fact, 96% of the participants supported utilizing the same methodology with other courses. In conclusion, this study provides evidence that Twitter is a useful tool in the educational process especially when different forms of media are combined. The study demonstrates Twitter’s ability to provide a collaborative platform for both faculty and students.
Masohiro Suzuki
Kanagawa Institute of Technology, Japan
Title: Technique of obtaining visually perceived positions using movements of users’ bodies
Time : 14:35-15:00

Biography:
Masahiro Suzuki received his B.A., M.A., and Ph.D. degrees in psychology from Chukyo University in Nagoya, Aichi, Japan in 1994, 1996, and 2002 respectively. He joined the Imaging Science and Engineering Laboratory of Tokyo Institute of Technology in Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan in 2003 as a postdoctoral researcher. He then joined the Human Media Research Center of Kanagawa Institute of Technology in Atsugi, Kanagawa, Japan in 2006 as a postdoctoral researcher. He will join the Department of Psychology of Tokiwa University in Mito, Ibaraki, Japan in April 2017 as an assistant professor. He is currently engaged in research on 3-D displays and augmented reality. Dr. Suzuki is a member of Japan Society of Kansei Engineering, Japanese Cognitive Science Society, Japanese Psychological Association, Optical Society of Japan, and Vision Society of Japan.
Abstract:
We proposed a technique of obtaining the visually perceived positions of virtual objects presented in front of the screens of 3-D displays, and evaluated it. Applications where users’ own bodies, which are actually seen by users unlike video captured images, interact with virtual objects are attractive applications of 3-D displays. Users expect interactions to be executed when their bodies are seen at the same positions of virtual objects because it is natural for them. Executing interactions when users’ bodies are at the visually perceived positions of virtual objects is the crucial requirement to interactions between the bodies and objects. Conventional techniques execute interaction when users’ bodies are at the positions calculated from binocular disparity of virtual objects. However, the visually perceived positions often differ from the positions calculated from binocular disparity, so that conventional techniques make it difficult to meet the requirement. In contrast to conventional techniques, the proposed technique can meet the requirement by obtaining the visually perceived positions of virtual objects from body movements. According to previous studies on body movements, the velocity of reaching movements as a function of time follows a bell curve. In the proposed technique, the velocity of reaching movements when users reach out to virtual objects is first fitted into a Gaussian function. The final positions of reaching movements are then obtained based on the fitted functions before the movements are finished because virtual objects are seen there. Therefore, the requirement is fulfilled by executing interactions when users’ bodies are at the positions obtained in last step. In the evaluation, we demonstrated the feasibility of the proposed technique by examining the accuracy and precision of the positions obtained with the proposed technique. We also demonstrated the usefulness of the proposed technique by examining the exactness of interaction executed with the proposed technique.
Md. Haidar Sharif
International University of Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Title: How to track unknown number of individual targets in videos?

Biography:
Md. Haidar Sharif received BSc in Electronics and Computer Science from the Jahangirnagar University (Bangladesh) in 2001, MSc in Computer Engineering from Duisburg-Essen University (Germany) in 2006, and PhD in Computer Science from the University of Science and Technology of Lille (France) in 2010. From January 2011 to January 2016, he had been working at Gediz University in Izmir (Turkey) as an Assistant Professor. He has been working at International University of Sarajevo (Bosnia and Herzegovina) since April 2016 as an Assistant Professor. He has his expertise in both computer vision and computer architecture.
Abstract:
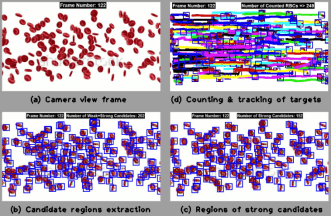
Target tracking, which aims at detecting the position of a moving object from video sequences, is a challenging research topic in computer vision. Obstacles in tracking targets can grow due to quick target motion, changing appearance patterns of target and scene, non-rigid target structures, dynamic illumination, inter-target and target-to-scene occlusions, and multi-target confusion. As selection of features affects the tracking results, it is eventful to select right features. Feature selection is closely related to the target representation. A target shape can be represented by a primitive geometric shape including rectangle, ellipse, circle, square, triangle, and point [1]. The efforts of tracking targets or objects in videos as efficient as possible are not new [1, 2, 3, 4]. A vast majority of the existing algorithms primarily differ in the way they use image features and model motion, appearance and shape of the target. In this discussion, we will discuss how to track unknown number of individual targets in videos by leveraging a spatiotemporal motion model of the movers. We will address our innovative idea [4] of how to extract the candidate regions, irrespective of movers' number in the scenes, from the silhouetted structures of movers' pixels. Silhouettes of movers obtained on capturing the local spatiotemporal motion patterns of movers, we can generate candidate regions in the candidate frames in a reflex manner. Candidate frame means a frame where a target template would be matched with one of its available movers. Weak candidate regions are deleted with the help of phase-correlation technique, while strong candidate regions are fed into a combined tracking algorithm of Hungarian process and Kalman filter. Since targets are searched in the strong candidate regions only, some well-established concepts (e.g., integral images [5] and brute force) are left out. Henceforth, search process gets super rapid as compared to brute force since comparative runtime reduced from O(n!) to O(n3) with problem size n. Complete trajectories of individual targets in 3D space are resulted in asymptotic runtime of O(n3). Figure 1 shows a sample output of our framework.
Pascal Lorenz
University of Haute-Alsace, France,
Title: Architectures of next generation wireless networks

Biography:
Pascal Lorenz (lorenz@ieee.org) received his M.Sc. (1990) and Ph.D. (1994) from the University of Nancy, France. Between 1990 and 1995 he was a research engineer at WorldFIP Europe and at Alcatel-Alsthom. He is a professor at the University of Haute-Alsace, France, since 1995. His research interests include QoS, wireless networks and high-speed networks. He is the author/co-author of 3 books, 3 patents and 200 international publications in refereed journals and conferences. He was Technical Editor of the IEEE Communications Magazine Editorial Board (2000-2006), Chair of Vertical Issues in Communication Systems Technical Committee Cluster (2008-2009), Chair of the Communications Systems Integration and Modeling Technical Committee (2003-2009), Chair of the Communications Software Technical Committee (2008-2010) and Chair of the Technical Committee on Information Infrastructure and Networking (2016-2017). He has served as Co-Program Chair of IEEE WCNC'2012 and ICC'2004, Executive Vice-Chair of ICC'2017, tutorial chair of VTC'2013 Spring and WCNC'2010, track chair of PIMRC'2012, symposium Co-Chair at Globecom 2007-2011, ICC 2008-2010, ICC'2014 and '2016. He has served as Co-Guest Editor for special issues of IEEE Communications Magazine, Networks Magazine, Wireless Communications Magazine, Telecommunications Systems and LNCS. He is associate Editor for International Journal of Communication Systems (IJCS-Wiley), Journal on Security and Communication Networks (SCN-Wiley) and International Journal of Business Data Communications and Networking, Journal of Network and Computer Applications (JNCA-Elsevier).
He is senior member of the IEEE, IARIA fellow and member of many international program committees. He has organized many conferences, chaired several technical sessions and gave tutorials at major international conferences. He was IEEE ComSoc Distinguished Lecturer Tour during 2013-2014.
Abstract:
Level: Survey, research issues
Theme: Quality of Service, Next generation networks, wireless networks
Summary: Emerging Internet Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms are expected to enable wide spread use of real time services such as VoIP and videoconferencing. The "best effort" Internet delivery cannot be used for the new multimedia applications. New technologies and new standards are necessary to offer Quality of Service (QoS) for these multimedia applications. Therefore new communication architectures integrate mechanisms allowing guaranteed QoS services as well as high rate communications.
The service level agreement with a mobile Internet user is hard to satisfy, since there may not be enough resources available in some parts of the network the mobile user is moving into. The emerging Internet QoS architectures, differentiated services and integrated services, do not consider user mobility. QoS mechanisms enforce a differentiated sharing of bandwidth among services and users. Thus, there must be mechanisms available to identify traffic flows with different QoS parameters, and to make it possible to charge the users based on requested quality. The integration of fixed and mobile wireless access into IP networks presents a cost effective and efficient way to provide seamless end-to-end connectivity and ubiquitous access in a market where the demand for mobile Internet services has grown rapidly and predicted to generate billions of dollars in revenue.
It covers to the issues of QoS provisioning in heterogeneous networks and Internet access over future wireless networks. It discusses the characteristics of the Internet, mobility and QoS provisioning in wireless and mobile IP networks. This tutorial also covers routing, security, baseline architecture of the inter-networking protocols and end to end traffic management issues.
Yuansong Qiao
Athlone Institute of Technology, Ireland
Title: Layer dependency aware multi-view video delivery

Biography:
Yuansong Qiao (John) is a Science Foundation Ireland funded Investigator working in the Software Research Institute (SRI) at Athlone Institute of Technology. He has over 15 years’ experience in computer networks and multimedia delivery. Currently, he is leading research teams working on two directions: 1) Information Centric Networking performance optimization for video distribution and IoT data processing; 2) Big Data analytics system optimization using Software Defined Networking technologies. He received his Ph.D. in Computer Applied Technology from the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISCAS), Beijing, China, in 2007. He completed a BSc and an MSc in Solid Mechanics from Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (BUAA), China in 1996 and 1999 respectively. After graduation He joined the ISCAS immediately where he held roles as a network administrator, research engineer and team leader in the R&D area of computer network, multimedia communication and network security protocols and products.
Abstract:
Multi-view video refers to a composite video stream generated by simultaneous capture from multiple cameras covering different portions, or views, of a scene. The Joint Video Team (JVT) has developed H.264/Multi-view Video Coding (MVC) to enhance the compression efficiency for multi-view video. Streaming of multiview video demands high bandwidth even after encoding. Any loss during transmission will have effect on the real-time quality of experience (QoE) of the end user due to the prediction structure used in H.264/MVC encoder. We will address the challenges in delivering MVC video and introduce MVC delivery technologies in both the traditional client/server based model and peer-to-peer (P2P) based model.
In the traditional client/server based streaming scenario, we have investigated the impacts of network fluctuations (e.g. packet losses) on the quality of streamed MVC video. The test results reveal unexpected differences in video quality amongst the streamed views. An MVC interleaving method is proposed to address this problem, which preferentially transmits the Network Abstraction Layer Unit (NALUs) with higher importance levels for decoding pictures. It reduces transmission errors on more important NALUs and hence enhances the streamed quality of different views.
In the P2P delivery scenario, we have investigated the optimisation problem of maximising outbound bandwidth utilisation of the peers in order to reduce bandwidth usage of the servers. The MVC layer dependency creates challenges in video layer sharing amongst the peers. The layers that can be shared between peers are limited by the layer dependency. A Bit-Torrent based layer-dependency-aware MVC video streaming system has been proposed and evaluated.

Biography:
Jane You is a full-professor in the Department of Computing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. She received her BEng. in Electronic Engineering from Xi’an Jiaotong University in 1986 and Ph.D in Computer Science from La Trobe University, Australia in 1992. She was awarded French Foreign Ministry International Postdoctoral Fellowship in 1993 and also obtained the Academic Certificate issued by French Education Ministry in 1994. She was a tenured senior lecturer at Griffith University, Australia before joining the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Her research interests include image processing, medical imaging, computer-aided detection/diagnosis, pattern recognition. So far, she has more than 200 research papers published. She is a team member for three US patents. Her recent work on retinal imaging has resulted in one US patent (2015), a Special Prize and Gold Medal with Jury’s Commendation at the 39th International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva (April 2011) and the second place in an international competition (SPIE Medical Imaging’2009 Retinopathy Online Challenge (ROC’2009)). She is also an associate editor of Pattern Recognition and other journals.
Abstract:
The rapid advances in electronic devices, digital imaging, information technology, computer systems and networks in recent years have stimulated the explosive growth of multimedia computing with diverse applications to different areas including medical service and healthcare. Equipped with various multimedia tools, techniques and services, computerized healthcare is emerging as an ever-increasing important multidisciplinary area which offers tremendous opportunities and excellent facilities to doctors, healthcare professionals and other eligible users to enhance performance by fully utilizing the rich health related multimedia data for effective decision making. Although the current achievements are exciting and the results can be powerful, it remains a challenging task to manage diversity of health related multimedia data on an open heterogeneous landscape (multi-modality, big volume, mobility, time series) efficiently, accurately, reliably and cost-effectively.
This talk presents a general multimedia-based framework to tackle the crucial issues on personalized healthcare. The new medical record e-book structure is proposed to facilitate flexible management of high-dimensional medical data on an open heterogeneous landscape. More specifically, our approach is revolved around three key aspects: 1) multimedia-based medical data management in the context of multi-modality, big volume, mobility and time series; 2) feature selection and fusion of high-dimensional medical data analysis and evaluation with quantitative measurement; 3) classification and decision support scheme for convenient, reliable, efficient and cost effective medical services. A prototype of smart mobile healthcare is developed to demonstrate the feasibility and potentials of the new solution which bridges the gap between data management, medical applications and multimedia computing in a robust environment.
Irfan Mehmood
Sejong University, South Korea
Title: Resource-Conscious frameworks for Multimedia Content Summarization and Information Prioritization

Biography:
Irfan Mehmood has been involved in IT industry and academia in Pakistan and South Korea for over 6 years. In Sep 2010, he started professional career as an android developer in Talented Earth Organization, http://www.teo-intl.com/, focusing on conducting design and build advanced applications for the Android platform. In 2015, he joined COMSATS institute of information and technology, Pakistan, as Assistant Professor, where he provided additional duties other than teaching such as project coordinator and supervising research activities of BS and MS students. Currently, he is working as an assistant professor in of department Computer Science and Engineering, School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sejong University. In addition, he is also coordinator of Global Computer Engineering Program, playing an active role in capacity building, improving teaching quality, and enhancing academia. Moreover, he is in strong research collaboration with various international research groups. He has published numerous articles in peer-reviewed international journals and conferences. He is serving as a professional reviewer for various reputed journals and conferences.
Abstract:
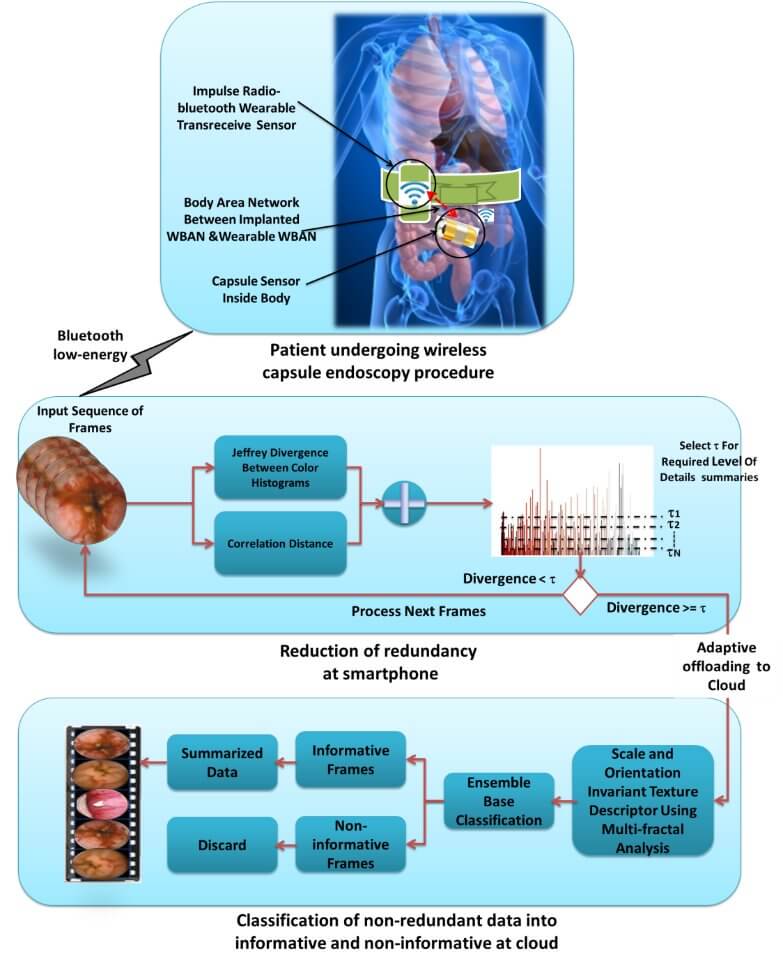
In recent years, there has been a tremendous increase in video capturing devices, which led to large personal and corporate digital video archives. This huge volume of video data became a source of inspiration for the development of vast numbers of applications such as visual surveillance, multimedia recommender systems, and context-aware advertising. The heterogeneity of video data, higher storage, processing cost, and communication requirements demand for a system that can efficiently manage and store huge amount of video data, while providing user-friendly access to stored data at the same time. To address this problem, multimedia summarization schemes have been proposed. Multimedia summarization refers to the extraction of keyframes, identifying most important and pertinent content. In various applications, video summarization can be conducted from the perspective of information prioritization, ranking chosen keyframes relative to their ability to describe the content of the video. A good video summary improves the effectiveness and efficiency of video archiving, cataloging, indexing, as well as increasing the usability of stored videos.
In this talk, video summarization in general and specifically in the context of prioritization (VSP) will be discussed. Varieties of algorithms, ranging from resource-conscious summarization framework to visual attention-based summarization methods are proposed. Four different VSP techniques are also proposed. The first summarization method is based on a light-weight visual attention model to efficiently extract diagnostically relevant keyframes from wireless capsule endoscopy videos. The second scheme proposes a resource-conscious summarization framework to manage remote sensing wireless capsule video data. The summarization is based on redundancy removal and classification of non-redundant frames into informative and non-informative frames. This framework utilizes cloud resources by adaptively offloading summarization tasks from mobile to cloud. The third and fourth proposed methods explore summarization in the context of prioritization in two different domains: 1) prioritization of brain magnetic resonance images; and 2) saliency-directed prioritization of visual data in wireless surveillance networks.
Masahiro Suzuki
Kanagawa Institute of Technology, Japan
Title: Technique of obtaining visually perceived positions using movements of users’ bodies

Biography:
Masahiro Suzuki received his B.A., M.A., and Ph.D. degrees in psychology from Chukyo University in Nagoya, Aichi, Japan in 1994, 1996, and 2002, respectively. He joined the Imaging Science and Engineering Laboratory of Tokyo Institute of Technology in Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan in 2003 as a postdoctoral researcher. He then joined the Human Media Research Center of Kanagawa Institute of Technology in Atsugi, Kanagawa, Japan in 2006 as a postdoctoral researcher. He will join the Department of Psychology of Tokiwa University in Mito, Ibaraki, Japan in April 2017 as an assistant professor. He is currently engaged in research on 3-D displays and augmented reality. Dr. Suzuki is a member of Japan Society of Kansei Engineering, Japanese Cognitive Science Society, Japanese Psychological Association, Optical Society of Japan, and Vision Society of Japan.
Abstract:
We proposed a technique of obtaining the visually perceived positions of virtual objects presented in front of the screens of 3-D displays, and evaluated it. Applications where users’ own bodies, which are actually seen by users unlike video captured images, interact with virtual objects are attractive applications of 3-D displays. Users expect interactions to be executed when their bodies are seen at the same positions of virtual objects because it is natural for them. Executing interactions when users’ bodies are at the visually perceived positions of virtual objects is the crucial requirement to interactions between the bodies and objects. Conventional techniques execute interaction when users’ bodies are at the positions calculated from binocular disparity of virtual objects. However, the visually perceived positions often differ from the positions calculated from binocular disparity, so that conventional techniques make it difficult to meet the requirement. In contrast to conventional techniques, the proposed technique can meet the requirement by obtaining the visually perceived positions of virtual objects from body movements. According to previous studies on body movements, the velocity of reaching movements as a function of time follows a bell curve. In the proposed technique, the velocity of reaching movements when users reach out to virtual objects is first fitted into a Gaussian function. The final positions of reaching movements are then obtained based on the fitted functions before the movements are finished because virtual objects are seen there. Therefore, the requirement is fulfilled by executing interactions when users’ bodies are at the positions obtained in last step. In the evaluation, we demonstrated the feasibility of the proposed technique by examining the accuracy and precision of the positions obtained with the proposed technique. We also demonstrated the usefulness of the proposed technique by examining the exactness of interaction executed with the proposed technique.
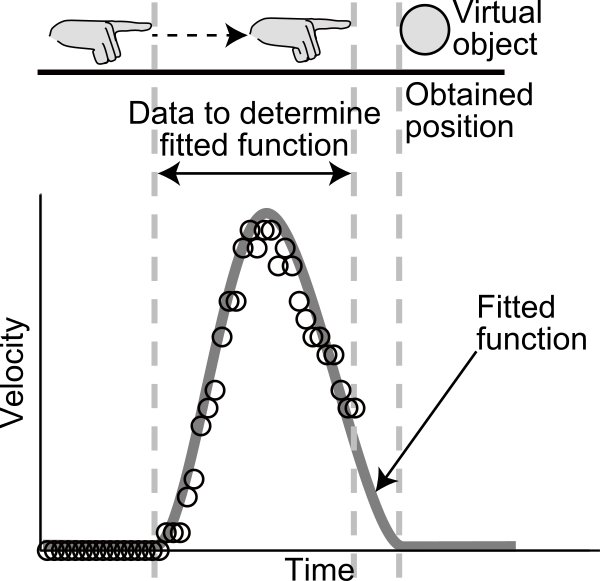
Yuxing Mao
Chongqing University, China
Title: Super-Resolution image reconstruction from multiple defocused images of stationary scene

Biography:
Yuxing Mao, he received the B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in radio electrical department from Beijing University, China,in 1989 and 1992, respectively. He got the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from Chongqing University, China, in 2004. He worked as a visiting scientist in the Center for Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence, CENPARMI, Concordia University, Canada, for one year in 2005. He is a senior member of China Society of Image and Graphics. He is currently a professor in School of Electrical Engineering, Chongqing University. His research interests include image processing and computer vision, and wireless sensor networks. He has published more than 40 papers in these fields
Abstract:
Super-resolution reconstruction (SRR) is an effective means to address the problem of insufficient image resolution in imaging applications. Existing SRR algorithms use well-focused images and ignore the value of defocused images generated by the imaging system during focusing. The starting point of the present study is to treat a defocused image as distribution and accumulation of scene information among different pixels of the detector, as well as a valid observation of the imaged subject; defocused images are the result of blurring a corresponding high resolution (HR) image using a point spread function (PSF) followed by downsampling. From this starting point, we used multiple defocused images to build an observation model for HR images and propose a SRR algorithm to approach the HR images. We have developed an image degradation model by analyzing optical lens imaging, used the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to estimate the PSF of the HR image, and used compressed sensing (CS) theory to implement SRR based on the non-coherent characteristics of multiple defocused images. Experiments demonstrate that our method can be used to obtain more information about details of a scene and improve the visual effect without adding any hardware facilities, improving the recognition and interpretation of the image subject.
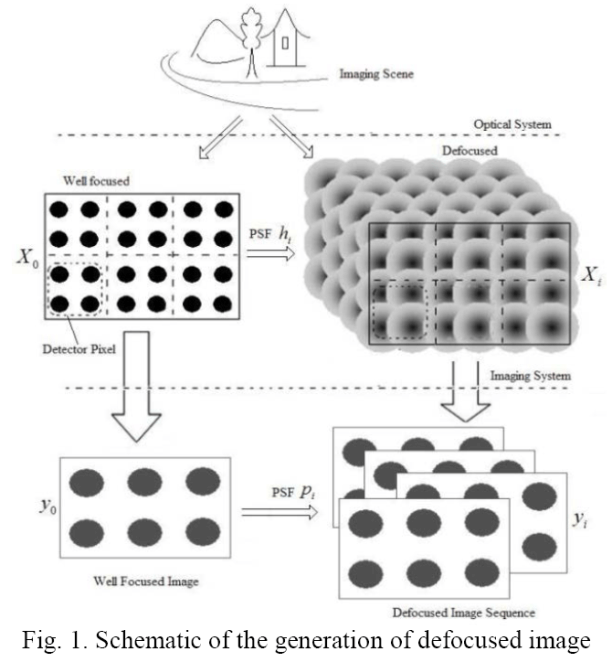
Kim Yong-Ho
Pukyong National University, SouthKorea
Title: Automatic key-frame extraction techniques using ERP responses to Real-time Video Watching: Testing N400 and P600 hypotheses

Biography:
Kim Yong-ho got his B. A., M. A. from Seoul National University. Mass Communications (1979, 1985) & Ph. D. from University of Wisconsin, Madison, School of Journalism(1991). After years of research fellowship at Korean Broadcasting Commission (1991-1995), he continues his career as Professor at Dongkuk Univ, & Pukyong National Univ. (1995-1997, 1998-present). His research papers were published in Electronic Library (2008), Communication Research (2010), Journal of The American Society for Information Science (2008, 2010), or were presented at such international conference as ICA, AEJMC, and HEF. Several books were published in Korean, one of which was awarded by the Ministry of Culture of the Korean national government in 2005. He has served for several scholarly organizations and worked for a journal of Broadcasting and Communication since 2012, as the Chief Editor. He is recently interested in the election poll censorship and the automatic key-visual extraction for video summarization.
Abstract:
Theoretical Background: In the linguistics literature on verbal semantic integration, the N400 effect refers to the fact that unexpected words will cause very low level of negative potentials in brainwave measures around 400ms(milli-seconds) after repeated presented settings and the P600 effect refers to the fact the unexpected words will cause very high level of positive potentials around 600ms.
Methods: Research literature on the video summarization indicates importance of the development of an un-obtrusive method of gathering external information of video users (Z. Lu and K. Grauman,, 2013; W. Ren and Y. Zhu,, 2008; A. Porselvi and S. Gunasundari, 2013). The analysis of event-related potentials (ERP) is such a method which extracts only a result of reaction with respect to certain stimuli from the brain waves.
Findings and Implications: We observed greater maximum potentials at the left prefrontal cortex (FP1, t = 6.930, p = 0.013), the left, right, and middle central lobes (C3, t = 4.670, p = 0.039; Cz, t = 9.818, p = 0.004; C4, t = 10.549 , p = 0.003), and the right and middle frontal-central lobes (FC4, t = 7.370, p = 0.011; FCz, t = 6.541, p = 0.016) of brain wave responses to topic-relevant shots. The right parietal and right temporal-parietal lobes (P8, t = 4.483, p =0.043; TP8, t = 5.326, p = 0.028). It is indisputable to further attempt this sort of ERP analysis of the EEG data during continuous viewing session using topic-relevance ratings from still image testing. Still, the surprisingly large effect of N400 and P600 at prefrontal lobe are asking for further refinement in the future experimental design.
Importance: We developed a method to import time code of video presentation to the EEG data with the topic-relevant information from ratings of topic-relevance for still-image captured from visual shots which were included in the videos. SNR(signal-to-noise ratio) of ERP analysis for the visual shots are about 12.2 well fit in the rage of 10-14 as professional consultant recommended for SNR.

Biography:
HaoWu received the B.E. degree and Ph.D from Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, in 2010 and 2015 respectively. From 2013 to 2015, he worked in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory as an research associate. Now, he works in Beijing Normal University as an assistant professor.
His current research interests include pattern recognition, image retrieval, image processing, and image recognition .His current research mainly focuses on image recognition.
Abstract:
Supervised retrieval model has been widely used in the field of computer vision and its high-quality result is supported by enough learning instances .However, in the process of experiments, it’s difficult to offer enough learning instances for each category. Especially for some special categories, the drawback is more obvious. So how to solve the problem has become one challenging problem.
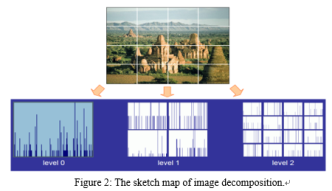
For this problem, we proposed one new model that can use candidate learning instances to replace the learning instances (In this paper, we mainly consider positive instances). On the one hand, the improved spatial pyramid matching function contributes to retrieve candidate learning instances effectively. On the other hand, an optimized SVM model make the most of candidate learning instances to keep the accuracy of retrieval. At last, we did enough groups of experiments using the new model. The experimental results show that our new model not only can reduce the number of learning instances but also can keep the high-quality of retrieval.

Hsien-Sheng Hsiao
National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan
Title: The manipulative augmented reality system for weather simulations in seamless learning environment

Biography:
Hsien-Sheng Hsiao received PhD degrees in information science from the University of National Chiao-Tung University in 1996. Currently, he is a professor with the Department of Technology Application and Human Resource Development, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan. His research interests include e-Learning, mobile learning, STEM education, and Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality for education.
Abstract:
This study focused on how to enhance the interactivity and usefulness of augmented reality (AR) by integrating manipulative interactive tools with a real-world environment. A manipulative AR (MAR) system, which included 3D interactive models and manipulative aids, was designed and developed to teach the unit “Understanding Weather” in a natural science course, and to bridge a formal learning environment (i.e. school), non-formal (i.e. at a museum), and informal learning environments (i.e. home). Sixty-four sixth-grade students (12–13 years old) from four classes in Taipei City were enrolled in a seven-week general studies course entitled “Natural and Life Science and Technology”, and they were divided into an experimental group (31 students who used the MAR system) and a control group (33 students who used multimedia teaching resources). After seven weeks of experiments, the results revealed that integrating the MAR system into inquiry-based field study made a greater positive impact on the students' academic achievement and motivation compared to the multimedia teaching resources installed on a tablet PC. Additionally, there were two interesting findings: (1) the MAR system offered effective learning materials relative to the multimedia teaching resources and (2) manipulative aids were an effective learning tool for interactivity and usefulness of AR. Besides, there were two meaningful suggestions associated with designing and developing the AR educational system for future researchers and designers, namely make it easy to use and include manipulative aids.
Yufang Tang
Shandong Normal University, China
Title: Sparse representation for image classification
Time : 15:00-15:25

Biography:
Yufang Tang has been a Lecturer at School of Communication of Shandong Normal University in China since 2015. He obtained his Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science and Technology (2007) and Master’s degree in Computer Application Technology (2010) at Shandong Normal University, and received his Doctorate degree in Signal and Information Processing at Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (2015). He is engaged in the research on Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining, etc.
Abstract:
As a new theory of signal sampling, sparse representation derived from compressed sensing, which is obviously different from Nyquist sampling theory. More and more image classification methods based on sparse representation have been proved to be effectively used in different fields, such as face recognition, hyper spectral image classification, handwriting recognition, medical image processing, etc. Image classification methods based on sparse representation has become a hotspot of research topic in recent years. Not only the research institutes, but also the governments and the militaries have invested lots of energy and finance in this attractive task. In this presentation, we intend to review its history and development tendency, and reveal our latest research progress on sparse representation for image classification.
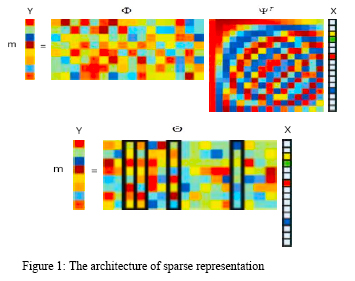
Li Liu
University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Title: Generating graphs from key points for near-duplicate document image matching
Time : 15:25-15:50

Biography:
Li Liu is a lecturer at the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology. She received the Ph.D. degree in pattern recognition and intelligent system from East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, in 2015. She was with the Centre for Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence (CENPARMI), Concordia University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, from 2013 to 2014 as a visiting doctoral student. Her research interests include pattern recognition, machine learning and image analysis
Abstract:
We propose a novel near-duplicate document image matching approach. Some keypoints are first detected from the image using the difference-of-Gaussian function. We then present a clustering method, based on which the keypoints are clustered into several groups. The number of clusters is determined automatically according to the distributions of the keypoints. Afterwards, a graph is generated whose nodes correspond to the obtained clusters and the edges describe the relationships between two clusters. Consequently, the problem of image matching is transformed to graph matching. To compute the similarity between two graphs, we build their association graph and then find the maximum weight clique. A thorough evaluation of the performance of the proposed approach is conducted on two different datasets. Promising experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and validity of this method.
- Young Researchers Forum
- Young Reseacher Forum
Session Introduction
Metehan Unal
Ankara University, Turkey
Title: A distant augmented reality system for cultural heritage sites using drones
Time : 16:10-16:30

Biography:
Metehan Unal holds a B.Sc. degree (honours) from Computer Engineering Department of Ankara University and now he is pursuing for an M.Sc. degree. He worked as trainee in Turkish Aerospace Industry in 2013. Now, he has been working as a Research Assistant in Ankara University since 2015. His research interests include Augmented Reality, Computer Graphics and Artificial Intelligence. He is also an enthusiastic Android developer.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Augmented Reality (AR) is a view that integrates the real world imagery with computer generated sounds, images or 3D objects. It has been possible by AR to place 3D reconstructions of buildings, which have been subject to wear and tear of thousands of years, on a historic site. In this way, cultural heritage sites can be better explained and handed on to future generations. Physical reconstruction in ruined cultural heritage sites can be financially costly and time consuming. In addition, site can be damaged during physical reconstruction. With state-of-art AR technology, 3D models can be placed in-situ without any damage, while increasing the appeal of the area for tourists and enthusiastic students.
The aim of this study is augmenting the video images received from mobile devices or drones with 3D models of Roman Bath which is one of the important cultural heritage sites in Ankara, Turkey.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: 3D model of Roman Bath were generated using reconstruction images drawn by expert archaeologists. Using Unity 3D Game Engine, this model was overlaid to the camera stream which is received from mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. The location services provided by these mobile devices were also used to place the model using actual GPS locations. Furthermore, an AR application was developed for drones to augment camera streams from a top-view, (Figure 1).
Findings: The developed application allows the users to display the models augmented on the camera view. The use of drones in this study brings a new dimension to Augmented Reality by adding a third eye to the user. We name this approach as ‘Distant Augmented Reality’.
Conclusion & Significance: The authors expect that such applications not only provide an entertaining way to learn about history but also preserve cultural heritage sites.
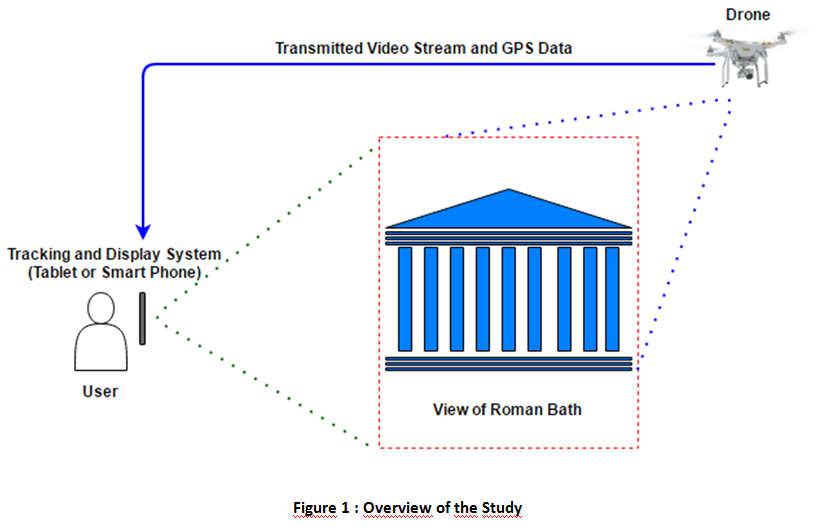
Yoshikatsu Nakajima
Keio University, Japan
Title: Viewpoint class based camera pose estimation and object recognition
Time : 16:30-16:50

Biography:
Yoshikatsu Nakajima received his B.E. degree in information and computer science from Keio University, Japan, in 2016. Since 2016, he has been a master student in the Department of Science and Technology and worked as a research assistant of Keio Program for Leading Graduate School at Keio University, Japan. He attended a lot of international and domestic conferences and won five awards in the two years since he started his research. In 2014, he had joined the start-up company Home-tudor Tomonokai as a developer and developed the on-line tutor system by himself using Ruby on Rails. His research interests include augmented reality, SLAM, object recognition, and computer vision.
Abstract:
Camera pose estimation with respect to target scenes is an important technology for superimposing virtual information in augmented reality. However, it is difficult to estimate the camera pose for all possible view angles because feature descriptors such as SIFT are not completely invariant from every perspective. We propose a novel method of robust camera pose estimation using multiple feature descriptor databases generated for each partitioned viewpoint in which the feature descriptor of each keypoint can be almost invariant. Our method estimates the viewpoint class for each input image using deep learning based on the set of training images prepared for each viewpoint class. We introduce two ways of preparing those images for deep learning and generating databases. In the first method, images are generated by Projection matrix to learn more robustly in the environment by changing those background. The second method uses real images to learn the entire environment around the plane pattern. Through the evaluation result, we confirmed that the number of the correct matches increased and the accuracy of camera pose estimation was improved compared to the conventional method.
Furthermore, we are trying on applying the concept of Viewpoint Class to the field of Object Recognition recently. Object recognition is one of the major research fields in computer vision and has been applied to various fields. In general, conventional methods are not robust in the obstacle and have a problem such that the accuracy is decreased when the camera stagnates at a poor position to the target object. We propose a novel method of object recognition that can be carried in real time by equally dividing the viewpoint around each object in the scene and impartially integrating the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) outputs from each Viewpoint Class (See Image). We confirmed its effectiveness through experiments.
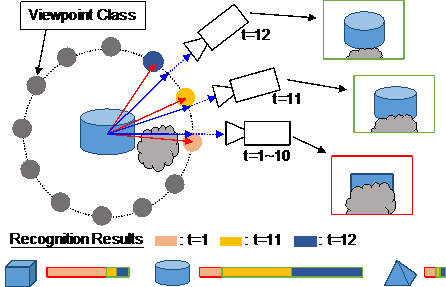
Yi bin Hou & Jin Wang
Beijing University of Technology, China
Title: Packet loss rate mapped to the quality of experience in the IOT network
Time : 16:50-17:10

Biography:
Jin Wang received a Bachelor’s degree in Software Engineering from Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, China, in 2012.6. And won the National Scholarship in 2010 and won the National Endeavor Fellowship in 2009. She received aMastersr graduate in Computer Application Technology in Shijiazhuang Tiedao University in 2015.1. And published manypapers, includingg ISTP, EI and SCI. Participate in three National Natural Science Fund Project (No: 61203377, 60963011, 61162009) and Jiangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 2009GZS0022), and the Special Research Foundation of Shijiazhuang Tiedao University (No: Z9901501, 20133007). She used to work at the computer center of the Navy General Hospital in 2015.4-2015.7 as an intern technician. Participate in Naval Logistics Project and anesthesia program (CHJ13L012). Now from 2015.4 she is in the school of software engineering, Department of information, Beijing University of Technology, read her PHD, Her research interests are the Internet of things and software engineering and Embedded and image and video quality assessment in distorting network.
Yibin Hou graduated from xi’ an Jiaotong university computer science department, with a master’s degree in engineering, graduated from the Netherlands EINDHOVEN university of technology department, received a doctor’s degree from the department of engineering. From 2002 to 2013 as vice President of Beijing university of technology. The Beijing university of technology, professor, doctoral supervisor, dean of the school of software, embedded computing, director of the institute, Beijing university of technology, deputy director of academic committee and secretary-general, Beijing Internet software and systems engineering technology research center director. His research interests have been Internet of things.
Abstract:
The Internet of things, including Internet technology, including wired and wireless networks.In this paper, we investigate on the QOE and packet loss rate of the network because QOE is important in the network and packet loss rate is the key point in many papers.In order to study the influence of packet loss on the users’ quality of experience QoE and establish the Mapping model of the two when the video transmit in the network, building a NS2 + MyEvalvid simulation platform, by the method of modifying QoS parameters to simulate different degrees of packet loss, focus on the influence of packet loss on QoE and establish the mapping model between them. Experimental results show that, packet loss has a significant influence on Quality of experience. Packet loss rate and the Quality of experience presents a nonlinear relationship, and use Matlab to establish the mapping model, this model’s accuracy is high, easy to operate, can real-time detect packet loss has influence on the user’s quality of experience (QoE). The contribution of this paper is first through research obtained packet loss has a significant effect on the video. Second, based on receiving the packet loss has a significant effect on QoE study and establish the mapping model of packet loss rate and the user’s quality of experience QoE. Next step is to set up considering network packet loss of video quality evaluation model, on the basis of considering the different packet loss rate and different content complexity has effects on QoE which conclude from packet loss has effects on QoE’s part, combine consider other factors such as different packet loss models to establish a video quality evaluation model consider the network packet loss, more accurate prediction of QoE is the future work. E-commerce, such as the Jingdong and Taobao's free trial center, has become a hot topic.
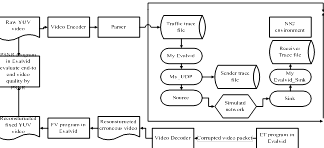
Fig. 1 MyEvalvid system structure
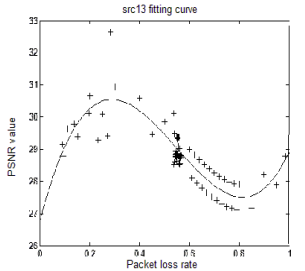
Fig. 23 Src13 fitting curve (PSNR)


























